Computer Vision
1. What is Computer Vision ?

Computer Vision is a field of Artificial Intelligence (AI) that enables computers to interpret and analyze visual information from the world, just like humans do. It involves processing, understanding, and extracting meaningful insights from images, videos, and real-world objects. Computer Vision relies on machine learning, deep learning, and neural networks to recognize patterns, detect objects, and perform tasks such as face recognition, object detection, image classification, and motion tracking.
Modern Computer Vision applications include autonomous vehicles (self-driving cars use CV to detect roads, obstacles, and pedestrians), medical imaging (AI-powered tools analyze X-rays and MRIs to detect diseases), security and surveillance (face recognition for access control), and retail automation (Amazon Go stores use CV for cashier-less checkouts). With advancements in deep learning and AI-powered image processing, Computer Vision is transforming industries, making machines smarter in understanding and interacting with the visual world.
2. Image Recognition
Image Recognition Image Recognition is a branch of Computer Vision that enables machines to identify and classify objects, people, places, or actions in images or videos. It uses artificial intelligence (AI), deep learning, and neural networks to analyze pixels, detect patterns, and recognize objects accurately. This technology powers applications like face recognition (e.g., unlocking phones with Face ID), automatic tagging in social media (e.g., Facebook auto-tagging), medical diagnosis (e.g., detecting tumors in X-rays), and retail automation (e.g., cashier-less stores like Amazon Go).
Image Recognition relies on Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), which learn patterns from large datasets to distinguish between different objects. Modern AI models, such as YOLO (You Only Look Once), ResNet, and MobileNet, improve recognition accuracy in real-time scenarios. With advancements in AI-powered image processing, Image Recognition is widely used in security, healthcare, automotive (self-driving cars), and e-commerce to enhance automation and decision-making.
With the rapid growth of AI and deep learning, Image Recognition has evolved into a highly efficient and accurate technology. Modern AI models, such as YOLO (You Only Look Once), Faster R-CNN, and Vision Transformers (ViTs), can process and identify objects in images and videos in real-time with high precision. These advancements have led to widespread applications across various industries.
For example, in healthcare, AI-powered image recognition helps in detecting diseases like cancer, pneumonia, and diabetic retinopathy through medical imaging. In automotive, self-driving cars use image recognition to detect pedestrians, traffic signs, and road conditions for safe navigation. In security and surveillance, facial recognition is used for identity verification and access control. Retail and e-commerce platforms also use image recognition for visual search and product recommendations. As AI continues to evolve, Image Recognition will play a crucial role in transforming industries, improving automation, and enhancing human-machine interaction.
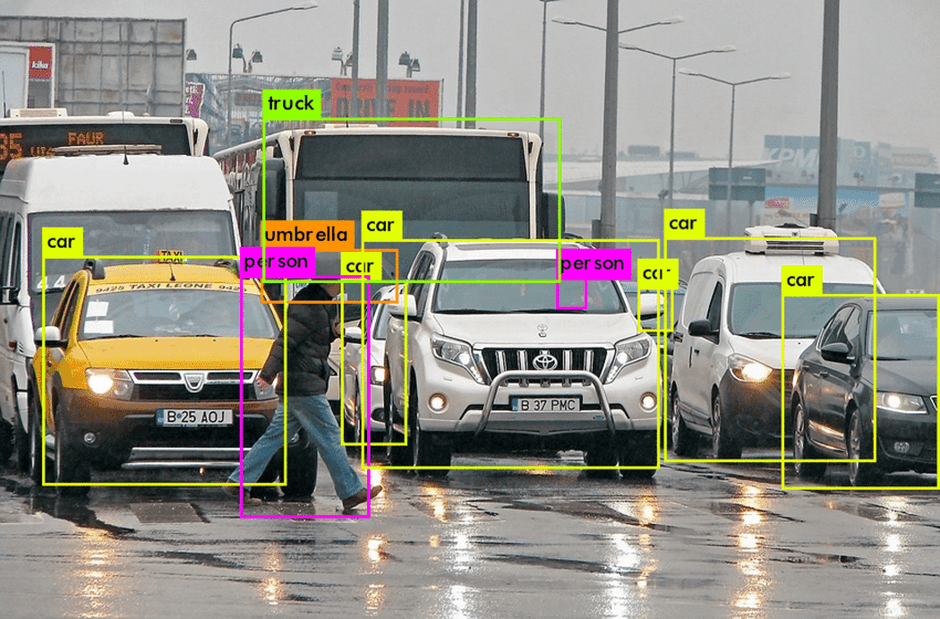
3. Object Detection
Object Detection is a key technology in Computer Vision that enables machines to not only recognize objects in an image but also locate their exact position within the image. Unlike Image Recognition, which simply classifies an object, Object Detection draws bounding boxes around detected objects and identifies their category. This technology is widely used in autonomous vehicles (detecting pedestrians, traffic lights), surveillance (identifying intruders), healthcare (analyzing medical scans), and retail (tracking inventory in smart stores)..
Modern Object Detection relies on deep learning models like YOLO (You Only Look Once), SSD (Single Shot MultiBox Detector), and Faster R-CNN, which process images in real-time with high accuracy. These models analyze pixel patterns, detect multiple objects simultaneously, and distinguish between different classes. As AI and deep learning continue to advance, Object Detection is becoming more efficient, allowing for innovations in robotics, augmented reality, and smart security systems.
Despite its advancements, Object Detection still faces challenges such as occlusions, variations in lighting, background clutter, and real-time processing constraints. For example, in autonomous driving, poor weather conditions like fog or rain can make object detection difficult. Similarly, in security applications, detecting objects in crowded areas or low-light environments requires highly optimized models. Researchers are constantly improving Object Detection by developing more efficient deep learning architectures, integrating transformers and self-supervised learning, and utilizing edge AI for faster, real-time processing.
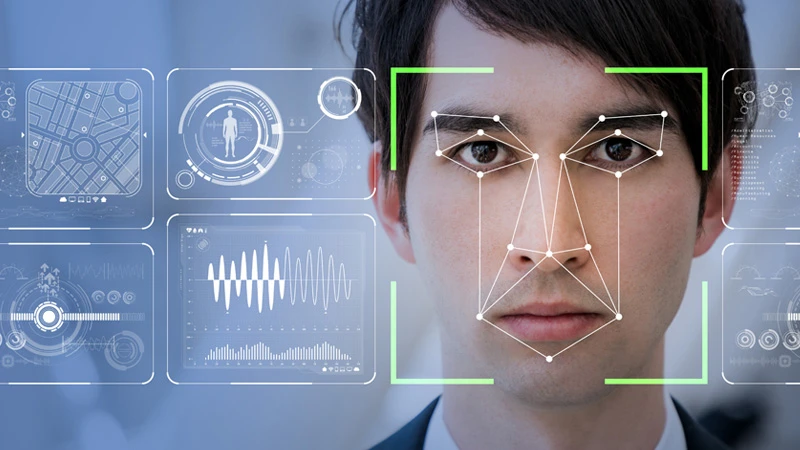
4. Face Recognition
Face Recognition is a biometric technology that identifies or verifies a person's identity using facial features. It works by analyzing key facial landmarks such as the distance between the eyes, nose shape, jawline, and other unique characteristics. Face Recognition is widely used in security systems (facial authentication in smartphones, surveillance cameras), law enforcement (criminal identification), banking (secure transactions), and even social media (auto-tagging in photos).
Modern Face Recognition relies on deep learning models like Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), FaceNet, and DeepFace, which extract facial features and compare them with a stored database. Techniques such as 2D and 3D face mapping, infrared detection, and AI-based anti-spoofing methods enhance accuracy and security. However, challenges like privacy concerns, bias in datasets, and vulnerability to spoofing attacks must be addressed for ethical and responsible use of this technology..
The future of Face Recognition is evolving rapidly with advancements in AI, deep learning, and edge computing. Emerging technologies like 3D facial recognition, thermal imaging, and liveness detection are improving accuracy and security, making it harder for spoofing attacks using photos or videos. In the coming years, Face Recognition will be integrated into smart cities, personalized advertising, healthcare (patient identification), and border security for seamless authentication.

5. Image Segmentation
Image Segmentation is a fundamental technique in Computer Vision that involves dividing an image into multiple regions or segments to simplify its analysis. Instead of processing the entire image as a whole, segmentation allows a system to focus on specific objects, boundaries, or patterns. It helps in tasks like object detection, medical imaging (tumor detection), autonomous driving (lane and pedestrian detection), and satellite image analysis.
There are different types of Image Segmentation, including Semantic Segmentation (categorizing each pixel into a class), Instance Segmentation (identifying individual objects), and Panoptic Segmentation (combining both approaches). Advanced methods use Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), Fully Convolutional Networks (FCNs), and U-Net architectures to achieve high accuracy in segmenting complex images. This technology plays a crucial role in enhancing computer vision applications across industries like healthcare, automotive, and agriculture. .
The future of Image Segmentation is evolving rapidly with advancements in deep learning, AI-powered models, and real-time processing techniques. With the rise of Transformer-based architectures like Vision Transformers (ViTs) and self-supervised learning, segmentation models are becoming more accurate and efficient. These improvements will enhance applications in medical imaging (early disease detection), autonomous vehicles (better obstacle recognition), and augmented reality (AR) for interactive experiences.

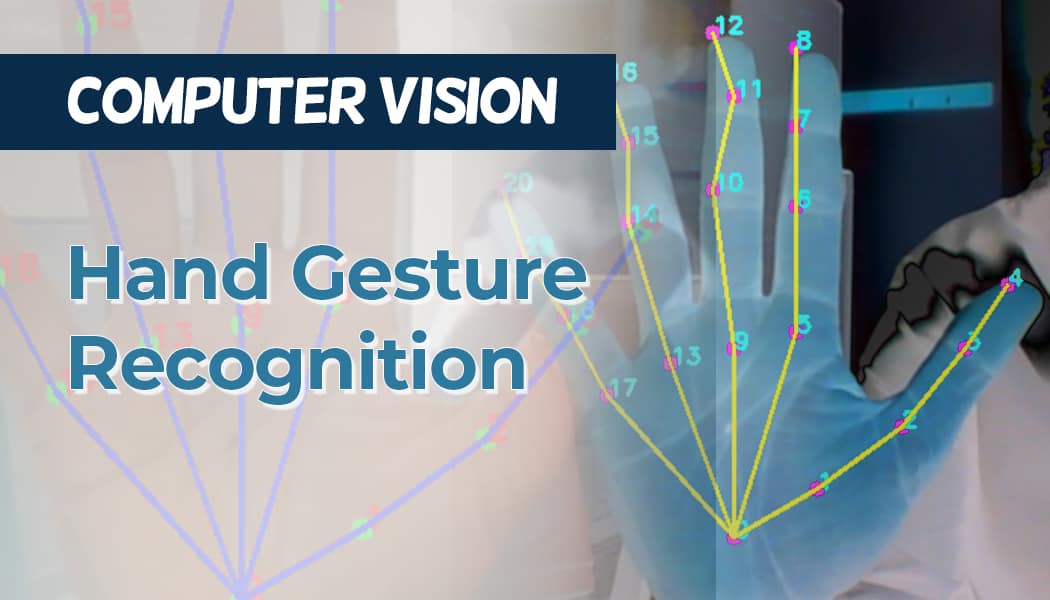
6. Gesture Recognition
Gesture Recognition is a technology in Computer Vision that enables machines to interpret human hand or body movements as commands. It allows users to interact with digital devices without physical touch, making it widely used in gaming (motion-controlled consoles), virtual reality (VR), sign language interpretation, smart home control, and automotive interfaces (gesture-based infotainment systems).
TThe future of Gesture Recognition is advancing with the integration of AI, deep learning, and augmented reality (AR), making interactions with technology more seamless and intuitive. With the rise of wearable devices, smart glasses, and AI-driven sensors, gesture control will become more accurate and widespread in industries like healthcare (touchless medical device control), automotive (gesture-based dashboard navigation), and gaming (more immersive VR experiences).
Emerging technologies like LiDAR sensors, depth cameras, and neural networks will enhance real-time recognition, even in low-light conditions or complex environments. However, challenges such as high computational costs, cultural variations in gestures, and privacy concerns need to be addressed. As AI continues to evolve, gesture recognition will redefine human-computer interaction, enabling a truly touchless and intuitive digital experience.
7. Optical Character Recognition (OCR)
Optical Character Recognition (OCR)
a is a technology that enables machines to read and convert printed, handwritten, or scanned text into digital form. OCR systems use computer vision and machine learning to recognize characters from images or documents, making them editable and searchable. This technology is widely used in digitizing books, extracting text from invoices, converting handwritten notes into digital text, and automating data entry processes.
Modern OCR systems use deep learning models like Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) and Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) to improve accuracy, even with complex fonts, poor image quality, or different handwriting styles. OCR is used in banking (automated check processing), healthcare (digitizing patient records), and security (passport scanning and ID verification). With advancements in AI, OCR is becoming more efficient in recognizing text across multiple languages and even extracting information from complex layouts like tables and forms..
The future of OCR is evolving with advancements in AI, deep learning, and natural language processing (NLP), making text recognition more accurate and efficient. Modern OCR systems are now capable of handling multilingual texts, complex document layouts, and even low-quality scans, improving accessibility and automation across industries. Real-time OCR is being integrated into mobile apps, smart glasses, and AI assistants, enabling instant text conversion for applications like live translation, smart document management, and accessibility tools for the visually impaired.
With the rise of edge computing and cloud-based OCR, businesses can process documents faster and more securely. However, challenges like text recognition in heavily distorted or handwritten scripts still need improvements. As AI continues to advance, OCR will play a key role in automating workflows, enhancing data extraction, and bridging the gap between physical and digital information.
.webp)
8. Medical Image Analysis
Medical Image Analysis is a specialized application of computer vision and artificial intelligence (AI) that helps in interpreting and analyzing medical images such as X-rays, MRIs, CT scans, and ultrasounds. It enables faster, more accurate disease detection, diagnosis, and treatment planning. AI-powered algorithms can identify tumors, fractures, infections, and organ abnormalities with high precision, assisting doctors in making better clinical decisions.
Deep learning models, especially Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), have revolutionized medical imaging by enhancing image segmentation, anomaly detection, and automated diagnosis. For example, AI can detect early signs of cancer in mammograms, classify brain tumors from MRI scans, or help radiologists analyze complex medical data efficiently. Medical image analysis reduces human errors, speeds up diagnosis, and improves patient outcomes, making it an essential tool in modern healthcare.
Recent advancements in AI-driven medical imaging have led to higher accuracy, real-time analysis, and automated diagnosis, significantly improving healthcare efficiency. Deep learning models, such as Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs), are now used to enhance image resolution, remove noise, and even generate synthetic medical images for training AI systems. Cloud-based medical imaging platforms enable doctors to collaborate remotely, allowing for faster second opinions and telemedicine applications..
However, despite its potential, medical image analysis faces challenges like data privacy concerns, regulatory approvals, and biases in AI models. Training AI systems requires large, diverse datasets, but medical data is often restricted due to privacy laws. Additionally, ensuring that AI models are explainable and interpretable is crucial for gaining trust in clinical settings. As research progresses, integrating AI with robotic-assisted surgeries and real-time diagnostics will further revolutionize the field, making healthcare more precise, efficient, and accessible worldwide.
Comments